Building a use case is a typical process that almost all successful business and IT Leaders want to and look forward to as an initial step to gather and weigh in their thoughts, analyze the pro and cons, and see if the proposed solution has the potential to meet their business goals, and make the final decision to buy in.
The higher the success of the use case the higher the confidence and motivation for the stakeholders.
Hence a use case is vital to all successful projects. However simple or complex the use case be, It has to be meticulously planned and executed in a systematic way.
Implementing Salesforce Data Cloud use cases can be complex. This blog post will walk you through the steps involved in implementing Salesforce Data Cloud use cases.
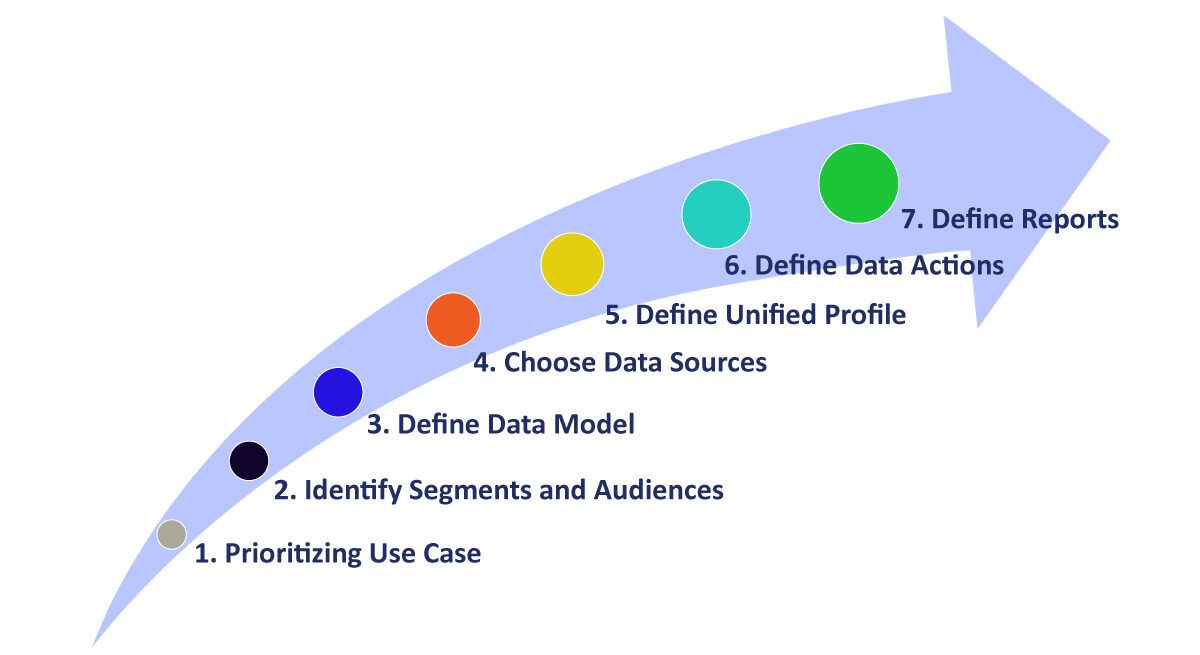
Step 1: Prioritize the Use Case
The first step in implementing a Salesforce Data Cloud use case is to align it to your business enablers’ vision. This means identifying the business goals the use case will help achieve. For example, the business’s goal is to use Salesforce Data Cloud to improve customer segmentation, personalize marketing campaigns, or identify at-risk customers.
Once the business goals are identified for the use case, we can start to develop a plan on how Salesforce Data Cloud can help achieve them.
Step 2: Identify Segments and Audiences
The next step is to identify the segments and audiences that you want to target with the selected use case. This will help you to determine the data that needs to be collected and the data actions that need to be performed.
For the goal of improving customer segmentation, the data should include customer demographics, purchase history, and engagement data with the business’s marketing campaigns.
You can then use this data to create segments of customers that are similar to each other in terms of their interests and needs.
Step 3: Define the Data Model
Once the segments and audiences that you are targeting are identified, a data model that will be used needs to be defined. This data model will be a blueprint for how the data will be stored and organized in Salesforce Data Cloud.
The data model should be designed to meet the specific needs of the use case and enable Customer 360 data model.
Step 4: Choose Data Sources
The next step is to choose the data sources that will be used to collect the data. Salesforce Data Cloud can ingest data from a variety of sources, including CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, and third-party data providers.
The choice of data sources will depend on the specific needs of the use case and also taking into consideration ingestion frequency which is batch, near real time or real time
Step 5: Define Unified Profile and Matching Rules
Once the data has been collected, you need to create a unified profile for each customer. A unified profile is a single view of a customer that includes data from all of the different data sources identified and used for the purposes of the use case.
Creating a unified profile can be complex, we need to define how to reconcile conflicting data and missing data.
Step 6: Define Data Actions
Once a unified profile is created for each customer, the data actions that you want to perform can be defined. Data actions are the tasks that Salesforce Data Cloud will perform on your data.
Step 7: Define Reporting Needs
Finally, you need to define your reporting needs. This will help determine the type of reports that need to be generated and the metrics that need to be tracked for the business leaders to analyze and take decisions.
For example, you might want to generate reports on customer engagement, customer churn, or marketing campaign effectiveness.
Conclusion
Implementing Salesforce Data Cloud use cases can be complex, but it can be a great way to convey to businesses how they can improve customer experience and gain insights into customers by mimicking real business-like scenarios and thus building the confidence to take decisions to implement Salesforce Data Cloud.
By following the steps outlined in this blog post, you can make the process of implementing Salesforce Data Cloud use cases easier and more successful.